1. 背景
引入jump label的背景,参考Linux: Jump label实现简析
在内核代码中,有很多分支判断条件,它们在绝大多数情形下,都是不成立的。尽管我们已经加上unlikely修饰来进行优化,但是,读取 condition 仍然要访问内存,仍然需要用到cache;另外,也会CPU分支预测失败。虽然少数这样的代码影响不大,但当这样的条件判断代码(如内核中大量的tracepoint)增多的时候,将对cache会造成很大压力,所有这些代码导致的cache miss,以及CPU分支预测失败,所造成的性能损失,就变得可观起来。因此,内核需要一种方案,来解决这样的问题。这个解决方案,就是本文描述的 Jump label。
2. 原理简介
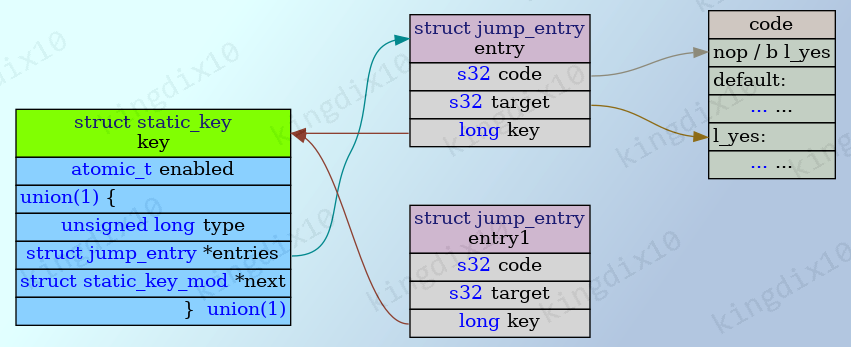
struct jump_entry的code记录要修改的地址,target记录需要跳转的地址。
以arch_static_branch为例,code指向的地址默认为nop指令。当修改struct static_key的值时,从entries找到struct jump_entry,构造一条b l_yes指令,然后写入到code指向的地址。arch_static_branch_jump则正好相反,code指向的地址默认为b l_yes。
| 数据 | 存储位置 |
|---|---|
| struct static_key | .bss |
| struct jump_entry | .rodata |
| code | .text |
静态分析时,只能通过反汇编得到struct jump_entry,然后得到struct static_key和代码的地址。如果只知道代码的地址或者struct static_key变量名,没有直接的办法来得到struct jump_entry的地址,只能通过遍历jump_table来找到对应的struct jump_entry。
动态分析时,可以通过struct static_key,找到struct jump_entry。
3. struct jump_entry
ARM64使能了CONFIG_HAVE_ARCH_JUMP_LABEL_RELATIVE,struct jump_entry中记录的是偏移量。
1/// include/linux/jump_label.h
2#ifdef CONFIG_HAVE_ARCH_JUMP_LABEL_RELATIVE
3
4struct jump_entry {
5 s32 code;
6 s32 target;
7 long key; // key may be far away from the core kernel under KASLR
8};
9
10static inline unsigned long jump_entry_code(const struct jump_entry *entry)
11{
12 return (unsigned long)&entry->code + entry->code;
13}
14
15static inline unsigned long jump_entry_target(const struct jump_entry *entry)
16{
17 return (unsigned long)&entry->target + entry->target;
18}
19
20static inline struct static_key *jump_entry_key(const struct jump_entry *entry)
21{
22 long offset = entry->key & ~3L;
23
24 return (struct static_key *)((unsigned long)&entry->key + offset);
25}
26
27#else
28/// struct jump_entry在arch/$ARCH/include/asm/jump_label.h中定义
29static inline unsigned long jump_entry_code(const struct jump_entry *entry)
30{
31 return entry->code;
32}
33
34static inline unsigned long jump_entry_target(const struct jump_entry *entry)
35{
36 return entry->target;
37}
38
39static inline struct static_key *jump_entry_key(const struct jump_entry *entry)
40{
41 return (struct static_key *)((unsigned long)entry->key & ~3UL);
42}
43
44#endif
4. arch_static_branch和arch_static_branch_jump
默认情况下,arch_static_branch总是返回false,arch_static_branch_jump总是返回true。
1/// arch/arm64/include/asm/jump_label.h
2static __always_inline bool arch_static_branch(struct static_key * const key,
3 const bool branch)
4{
5 asm_volatile_goto(
6 /// 声明标号1,对应指令为nop,编译时会优化,运行时直接执行后续代码
7 "1: nop \n\t"
8 /// 链接时放到__jump_table段
9 " .pushsection __jump_table, \"aw\" \n\t"
10 /// struct jump_entry地址按8字节对齐,不同处理器架构可能不一样,但地址都是偶数
11 " .align 3 \n\t"
12 /// jump_entry.code记录标号1和当前地址的差值,可能为负值
13 /// jump_entry.target记录当前地址和l_yes的差值,可能为负值
14 " .long 1b - ., %l[l_yes] - . \n\t"
15 /// jump_entry.target记录struct static_key和当前地址的差值,低位记录branch
16 /// 运行时可以使用jump_entry_key获取struct static_key的地址
17 " .quad %c0 - . \n\t"
18 " .popsection \n\t"
19 : : "i"(&((char *)key)[branch]) : : l_yes);
20
21 return false;
22l_yes:
23 return true;
24}
25
26static __always_inline bool arch_static_branch_jump(struct static_key * const key,
27 const bool branch)
28{
29 asm_volatile_goto(
30 /// 编译时会优化,直接跳转到l_yes执行代码
31 "1: b %l[l_yes] \n\t"
32 " .pushsection __jump_table, \"aw\" \n\t"
33 " .align 3 \n\t"
34 " .long 1b - ., %l[l_yes] - . \n\t"
35 " .quad %c0 - . \n\t"
36 " .popsection \n\t"
37 : : "i"(&((char *)key)[branch]) : : l_yes);
38
39 return false;
40l_yes:
41 return true;
42}
特别说明下(&((char *)key)[branch]),这个是取key的地址,并强制转为char *类型。
- 当
branch = false时,%c0 - .就是key的地址与当前位置的差值。 - 当
branch = true时,%c0 - .是key的地址与当前位置的差值再加1(char *偏移量为1)。
这样最低位就记录了branch的值。
4.1. struct jump_entry存储位置
从vmlinux.lds可以看到__jump_table在.rodata段。这是链接时的布局,在Linux启动时,jump_label_init会重新对jump_table进行排序。
1/// aarch64-linux-gnu-objdump -d -j .rodata vmlinux | less
2ffff80008137de00 <__start___jump_table>:
3ffff80008137de00: fec96fd4 .word 0xfec96fd4
4ffff80008137de04: fec96fd8 .word 0xfec96fd8
5ffff80008137de08: 00b132a8 .word 0x00b132a8
6ffff80008137de0c: 00000000 .word 0x00000000
7
8ffff80008137de10: fec9707c .word 0xfec9707c
9ffff80008137de14: fec97090 .word 0xfec97090
10ffff80008137de18: 00a56881 .word 0x00a56881
11ffff80008137de1c: 00000000 .word 0x00000000
5. 从struct jump_entry到struct static_key
根据前边的jump_entry_code、jump_entry_target和jump_entry_key的实现,计算如下:
1python3
2>>> hex(0xffff80008137de00 - 0x100000000 + 0xfec96fd4)
3'0xffff800080014dd4' /// code
4>>> hex(0xffff80008137de04 - 0x100000000 + 0xfec96fd8)
5'0xffff800080014ddc' /// target
6>>> hex(0xffff80008137de08 + 0x00b132a8)
7'0xffff800081e910b0' /// key
可以看到struct static_key在bss段。使用DEFINE_STATIC_KEY_TRUE和DEFINE_STATIC_KEY_FALSE声明的变量都会在bss段。
1/// readelf -S vmlinux
2[29] .bss NOBITS ffff800081e2a000 01e39a00
3
4/// aarch64-linux-gnu-nm -n vmlinux | grep -w gic_nonsecure_priorities
5ffff800081e910b0 B gic_nonsecure_priorities
根据反汇编和0xffff800080014dd4这个地址,可以找到代码对应的是arch_local_irq_disable函数。
1grep -C 20 ffff800080014dd4 vmlinux.dis
6. arch_local_irq_disable源码
1/// arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h
2static inline void arch_local_irq_enable(void)
3{
4 if (__irqflags_uses_pmr()) {
5 __pmr_local_irq_enable();
6 } else {
7 __daif_local_irq_enable();
8 }
9}
10
11static __always_inline void __daif_local_irq_disable(void)
12{
13 barrier();
14 asm volatile("msr daifset, #3");
15 barrier();
16}
17
18static __always_inline void __pmr_local_irq_disable(void)
19{
20 if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM64_DEBUG_PRIORITY_MASKING)) {
21 u32 pmr = read_sysreg_s(SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1);
22 WARN_ON_ONCE(pmr != GIC_PRIO_IRQON && pmr != GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF);
23 }
24
25 barrier();
26 write_sysreg_s(GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF, SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1);
27 barrier();
28}
29
30static inline void arch_local_irq_disable(void)
31{
32 if (__irqflags_uses_pmr()) {
33 __pmr_local_irq_disable();
34 } else {
35 __daif_local_irq_disable();
36 }
37}
关注write_sysreg_s(GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF, SYS_ICC_PMR_EL1);。
1/// arch/arm64/include/asm/sysreg.h
2#define write_sysreg_s(v, r) do { \
3 u64 __val = (u64)(v); \
4 u32 __maybe_unused __check_r = (u32)(r); \
5 asm volatile(__msr_s(r, "%x0") : : "rZ" (__val)); \
6} while (0)
GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF用到了static_branch_unlikely,实际走的是branch = arch_static_branch(&(x)->key, false)。
1/// arch/arm64/include/asm/ptrace.h
2/*
3 * PMR values used to mask/unmask interrupts.
4 *
5 * GIC priority masking works as follows: if an IRQ's priority is a higher value
6 * than the value held in PMR, that IRQ is masked. Lowering the value of PMR
7 * means masking more IRQs (or at least that the same IRQs remain masked).
8 *
9 * To mask interrupts, we clear the most significant bit of PMR.
10 *
11 * Some code sections either automatically switch back to PSR.I or explicitly
12 * require to not use priority masking. If bit GIC_PRIO_PSR_I_SET is included
13 * in the priority mask, it indicates that PSR.I should be set and
14 * interrupt disabling temporarily does not rely on IRQ priorities.
15 */
16#define GIC_PRIO_IRQON 0xe0
17#define __GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF (GIC_PRIO_IRQON & ~0x80)
18#define __GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF_NS 0xa0
19#define GIC_PRIO_PSR_I_SET (1 << 4)
20
21#define GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF \
22 ({ \
23 extern struct static_key_false gic_nonsecure_priorities;\
24 u8 __prio = __GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF; \
25 \
26 if (static_branch_unlikely(&gic_nonsecure_priorities)) \
27 __prio = __GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF_NS; \
28 \
29 __prio; \
30 })
7. static_branch_likely和static_branch_unlikely
内核文档Documentation/staging/static-keys.rst。
1 DEPRECATED API:
2
3 The use of 'struct static_key' directly, is now DEPRECATED. In addition
4 static_key_{true,false}() is also DEPRECATED. IE DO NOT use the following::
5
6 struct static_key false = STATIC_KEY_INIT_FALSE;
7 struct static_key true = STATIC_KEY_INIT_TRUE;
8 static_key_true()
9 static_key_false()
10
11 The updated API replacements are::
12
13 DEFINE_STATIC_KEY_TRUE(key);
14 DEFINE_STATIC_KEY_FALSE(key);
15 DEFINE_STATIC_KEY_ARRAY_TRUE(keys, count);
16 DEFINE_STATIC_KEY_ARRAY_FALSE(keys, count);
17 static_branch_likely()
18 static_branch_unlikely()
static_branch_likely和static_branch_unlikely实现,以如下示例代码进行分析。
1if (x) {
2 codeA
3} else {
4 codeB
5}
详见注释。
1/// include/linux/jump_label.h
2#ifdef CONFIG_JUMP_LABEL
3
4/*
5 * Combine the right initial value (type) with the right branch order
6 * to generate the desired result.
7 *
8 *
9 * type\branch| likely (1) | unlikely (0)
10 * -----------+-----------------------+------------------
11 * | |
12 * true (1) | ... | ...
13 * | NOP | JMP L
14 * | <br-stmts> | 1: ...
15 * | L: ... |
16 * | |
17 * | | L: <br-stmts>
18 * | | jmp 1b
19 * | |
20 * -----------+-----------------------+------------------
21 * | |
22 * false (0) | ... | ...
23 * | JMP L | NOP
24 * | <br-stmts> | 1: ...
25 * | L: ... |
26 * | |
27 * | | L: <br-stmts>
28 * | | jmp 1b
29 * | |
30 * -----------+-----------------------+------------------
31 *
32 * The initial value is encoded in the LSB of static_key::entries,
33 * type: 0 = false, 1 = true.
34 *
35 * The branch type is encoded in the LSB of jump_entry::key,
36 * branch: 0 = unlikely, 1 = likely.
37 *
38 * This gives the following logic table:
39 *
40 * enabled type branch instuction
41 * -----------------------------+-----------
42 * 0 0 0 | NOP
43 * 0 0 1 | JMP
44 * 0 1 0 | NOP
45 * 0 1 1 | JMP
46
47 * 1 0 0 | JMP
48 * 1 0 1 | NOP
49 * 1 1 0 | JMP
50 * 1 1 1 | NOP
51 *
52 * Which gives the following functions:
53 *
54 * dynamic: instruction = enabled ^ branch
55 * static: instruction = type ^ branch
56 *
57 * See jump_label_type() / jump_label_init_type().
58 */
59
60#define static_branch_likely(x) \
61({ \
62 bool branch; \
63 if (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(*x), struct static_key_true)) \
64 /// 1 1 1 | NOP
65 /// x为true的可能性大,直接执行codeA
66 branch = !arch_static_branch(&(x)->key, true); \
67 else if (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(*x), struct static_key_false)) \
68 /// 0 0 1 | JMP
69 /// x为false的可能性大,更可能直接跳转到codeB,可能把codeB放到codeA之前进行编译
70 branch = !arch_static_branch_jump(&(x)->key, true); \
71 else \
72 branch = ____wrong_branch_error(); \
73 likely_notrace(branch); \
74})
75
76#define static_branch_unlikely(x) \
77({ \
78 bool branch; \
79 if (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(*x), struct static_key_true)) \
80 /// 1 1 0 | JMP
81 /// x为true的可能性小,直接跳转到codeB的可能性大,可能把codeB放到codeA之前进行编译
82 branch = arch_static_branch_jump(&(x)->key, false); \
83 else if (__builtin_types_compatible_p(typeof(*x), struct static_key_false)) \
84 /// 0 0 0 | NOP
85 /// x为false的可能性小,执行codeB的可能性小
86 branch = arch_static_branch(&(x)->key, false); \
87 else \
88 branch = ____wrong_branch_error(); \
89 unlikely_notrace(branch); \
90})
91
92#else /* !CONFIG_JUMP_LABEL */
8. 反汇编分析
这里额外做一下说明:
-
使用
grep -C2 -w arch_local_irq_disable vmlinux.dis可以看到反汇编中有很多bl arch_local_irq_disable,并不是每次调用都进行了内联,而是在单个文件中只有一份汇编指令,函数调用时使用bl指令。static inline会在.c文件中生成一份指令,inline只是建议编译器进行内联,并不保证内联。 -
__irqflags_uses_pmr内有alternative_has_cap_unlikely,编译器进行了代码重排,反汇编中__daif_local_irq_disable在__pmr_local_irq_disable之前。alternative_has_cap_unlikely与arch_static_branch类似,优先返回false。ALTERNATIVE宏也是一种动态代码替换的技术,详见Linux ARM64架构 动态替换 altinstructions。
重点关注__pmr_local_irq_disable部分汇编代码即可。
1/// grep -C 20 ffff800080014dd4 vmlinux.dis
2ffff800080014dc8 <arch_local_irq_disable>:
3alternative_has_cap_unlikely():
4/data/eel/source/kernel/linux-6.6/arch/arm64/include/asm/alternative-macros.h:250
5ffff800080014dc8: d503201f nop /// __irqflags_uses_pmr
6__daif_local_irq_disable():
7/data/eel/source/kernel/linux-6.6/arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h:62
8ffff800080014dcc: d50343df msr daifset, #0x3 /// __daif_local_irq_disable
9/data/eel/source/kernel/linux-6.6/arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h:64
10ffff800080014dd0: 14000008 b ffff800080014df0 <arch_local_irq_disable+0x28>
11/// 以下开始是__pmr_local_irq_disable的指令
12arch_static_branch(): /// 对应GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF宏,由static_branch_unlikely调用
13/data/eel/source/kernel/linux-6.6/arch/arm64/include/asm/jump_label.h:21
14/// gic_nonsecure_priorities为struct static_key_false,默认取__GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF(0x60)
15/// 使能时,ffff800080014dd4处替换为 b ffff800080014ddc,取__GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF_NS(0xa0)
16ffff800080014dd4: d503201f nop
17ffff800080014dd8: 14000003 b ffff800080014de4 <arch_local_irq_disable+0x1c>
18__pmr_local_irq_disable():
19/data/eel/source/kernel/linux-6.6/arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h:74
20ffff800080014ddc: 52801400 mov w0, #0xa0 // #160
21ffff800080014de0: 14000002 b ffff800080014de8 <arch_local_irq_disable+0x20>
22ffff800080014de4: 52800c00 mov w0, #0x60 // #96
23ffff800080014de8: 92401c00 and x0, x0, #0xff
24ffff800080014dec: d5184600 msr s3_0_c4_c6_0, x0
25arch_local_irq_disable():
26/data/eel/source/kernel/linux-6.6/arch/arm64/include/asm/irqflags.h:85
27ffff800080014df0: d65f03c0 ret
与示例代码进行对应:
1if (static_branch_unlikely(x)) {
2ffff800080014dd4: b ffff800080014ddc /// 默认为nop,需要运行时替换
3} else {
4ffff800080014dd8: b ffff800080014de4
5}
8.1. 执行流
1/// 这部分本质上是__pmr_local_irq_enable的指令
2/// gic_nonsecure_priorities为struct static_key_false,默认取__GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF(0x60)
3/// 使能时,ffff800080014dd4处替换为 b ffff800080014ddc,取__GIC_PRIO_IRQOFF_NS(0xa0)
4默认 替换后
5ffff800080014dd4 ffff800080014dd4
6ffff800080014dd8 ffff800080014ddc *
7ffff800080014de4 ffff800080014de0 *
8ffff800080014de8 ffff800080014de8
9ffff800080014dec ffff800080014dec
10写入0x60 写入0xa0
9. jump_label_init
启动过程中,在jump_label_init中,根据jump_table来初始化static_key。
1/// kernel/jump_label.c
2void __init jump_label_init(void)
3{
4 struct jump_entry *iter_start = __start___jump_table;
5 struct jump_entry *iter_stop = __stop___jump_table;
6 struct static_key *key = NULL;
7 struct jump_entry *iter;
8
9 /*
10 * Since we are initializing the static_key.enabled field with
11 * with the 'raw' int values (to avoid pulling in atomic.h) in
12 * jump_label.h, let's make sure that is safe. There are only two
13 * cases to check since we initialize to 0 or 1.
14 */
15 BUILD_BUG_ON((int)ATOMIC_INIT(0) != 0);
16 BUILD_BUG_ON((int)ATOMIC_INIT(1) != 1);
17
18 if (static_key_initialized)
19 return;
20
21 cpus_read_lock();
22 jump_label_lock();
23 /// 按jump_entry指向static_key的地址,将jump_entry进行升序排列
24 jump_label_sort_entries(iter_start, iter_stop);
25
26 for (iter = iter_start; iter < iter_stop; iter++) {
27 struct static_key *iterk;
28 bool in_init;
29
30 /* rewrite NOPs */
31 if (jump_label_type(iter) == JUMP_LABEL_NOP)
32 arch_jump_label_transform_static(iter, JUMP_LABEL_NOP);
33
34 /// 是不是在__init_begin, __init_end之间
35 in_init = init_section_contains((void *)jump_entry_code(iter), 1);
36 /// in_init的static_key只能在初始化阶段update,见jump_label_update和__jump_label_update
37 jump_entry_set_init(iter, in_init);
38
39 iterk = jump_entry_key(iter);
40 /// 排序后,指向同一static_key的jump_entry会连续存放
41 /// static_key只需记录第一个jump_entry
42 if (iterk == key)
43 continue;
44
45 key = iterk;
46 static_key_set_entries(key, iter);
47 }
48 static_key_initialized = true;
49 jump_label_unlock();
50 cpus_read_unlock();
51}
9.1. static_key_set_entries
1/// kernel/jump_label.c
2/***
3 * A 'struct static_key' uses a union such that it either points directly
4 * to a table of 'struct jump_entry' or to a linked list of modules which in
5 * turn point to 'struct jump_entry' tables.
6 *
7 * The two lower bits of the pointer are used to keep track of which pointer
8 * type is in use and to store the initial branch direction, we use an access
9 * function which preserves these bits.
10 */
11static void static_key_set_entries(struct static_key *key,
12 struct jump_entry *entries)
13{
14 unsigned long type;
15
16 WARN_ON_ONCE((unsigned long)entries & JUMP_TYPE_MASK);
17 type = key->type & JUMP_TYPE_MASK;
18 key->entries = entries;
19 key->type |= type;
20}
entries和type在union中,这里用低位记录type,高位记录entries。取值时使用掩码进行运算。见static_key_entries、static_key_type、static_key_set_entries等函数。
1/// include/linux/jump_label.h
2struct static_key {
3 atomic_t enabled;
4#ifdef CONFIG_JUMP_LABEL
5/*
6 * Note:
7 * To make anonymous unions work with old compilers, the static
8 * initialization of them requires brackets. This creates a dependency
9 * on the order of the struct with the initializers. If any fields
10 * are added, STATIC_KEY_INIT_TRUE and STATIC_KEY_INIT_FALSE may need
11 * to be modified.
12 *
13 * bit 0 => 1 if key is initially true
14 * 0 if initially false
15 * bit 1 => 1 if points to struct static_key_mod
16 * 0 if points to struct jump_entry
17 */
18 union {
19 unsigned long type;
20 struct jump_entry *entries;
21 struct static_key_mod *next;
22 };
23#endif /* CONFIG_JUMP_LABEL */
24};
10. 值的更新
1/// include/kernel/jump_label.h
2/*
3 * Advanced usage; refcount, branch is enabled when: count != 0
4 */
5
6#define static_branch_inc(x) static_key_slow_inc(&(x)->key)
7#define static_branch_dec(x) static_key_slow_dec(&(x)->key)
8#define static_branch_inc_cpuslocked(x) static_key_slow_inc_cpuslocked(&(x)->key)
9#define static_branch_dec_cpuslocked(x) static_key_slow_dec_cpuslocked(&(x)->key)
10
11/*
12 * Normal usage; boolean enable/disable.
13 */
14
15#define static_branch_enable(x) static_key_enable(&(x)->key)
16#define static_branch_disable(x) static_key_disable(&(x)->key)
17#define static_branch_enable_cpuslocked(x) static_key_enable_cpuslocked(&(x)->key)
18#define static_branch_disable_cpuslocked(x) static_key_disable_cpuslocked(&(x)->key)
这些函数最终都会调用jump_label_update,jump_label_update会根据struct static_key找到struct jump_entry。
以ARM64为例,之后会通过调用arch_jump_label_transform进行更新。
1/// arch/arm64/kernel/jump_label.c
2void arch_jump_label_transform(struct jump_entry *entry,
3 enum jump_label_type type)
4{
5 void *addr = (void *)jump_entry_code(entry);
6 u32 insn;
7
8 /// 根据type生成要替换的指令
9 if (type == JUMP_LABEL_JMP) {
10 insn = aarch64_insn_gen_branch_imm(jump_entry_code(entry),
11 jump_entry_target(entry),
12 AARCH64_INSN_BRANCH_NOLINK);
13 } else {
14 insn = aarch64_insn_gen_nop();
15 }
16
17 /// 修改代码段,写入新的指令
18 aarch64_insn_patch_text_nosync(addr, insn);
19}
aarch64_insn_patch_text_nosync最后会调用__aarch64_insn_write来完成代码段的更新。
1/// arch/arm64/kernel/patching.c
2static int __kprobes __aarch64_insn_write(void *addr, __le32 insn)
3{
4 void *waddr = addr;
5 unsigned long flags = 0;
6 int ret;
7
8 raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&patch_lock, flags);
9 waddr = patch_map(addr, FIX_TEXT_POKE0); /// 使用fixmap建立可写映射
10
11 /// 修改代码段,写入新的指令
12 ret = copy_to_kernel_nofault(waddr, &insn, AARCH64_INSN_SIZE);
13
14 patch_unmap(FIX_TEXT_POKE0);
15 raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&patch_lock, flags);
16
17 return ret;
18}
对于内核镜像,由于内核的代码段被映射为只读,这里patch_map会新建一个可写映射,然后进行代码修改。
对于驱动模块的代码,如果使能了CONFIG_STRICT_MODULE_RWX,也会新建映射。否则,patch_map直接返回指令地址。
10.1. 更新时机
根据struct static_key的特性,其更新的时机由如下几种:
- 启动阶段使用
__setup或early_param - 驱动probe时使用
module_param - 运行时,通过sysfs/procfs/debugfs导出的节点配置




