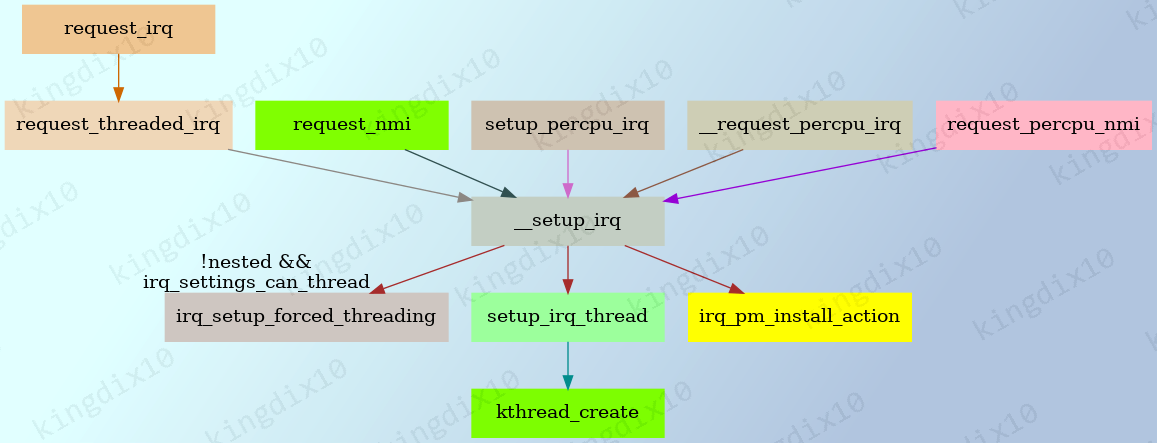
1. 申请中断
__setup_irq是用于设置和注册中断的核心函数,它是request_threaded_irq等函数的内部实现。
1.1. irqaction
handler和thread_fn是struct irqaction的两个重要成员,由程序员指定或在__setup_irq中自动设置,
在中断发生后的处理函数被调用。
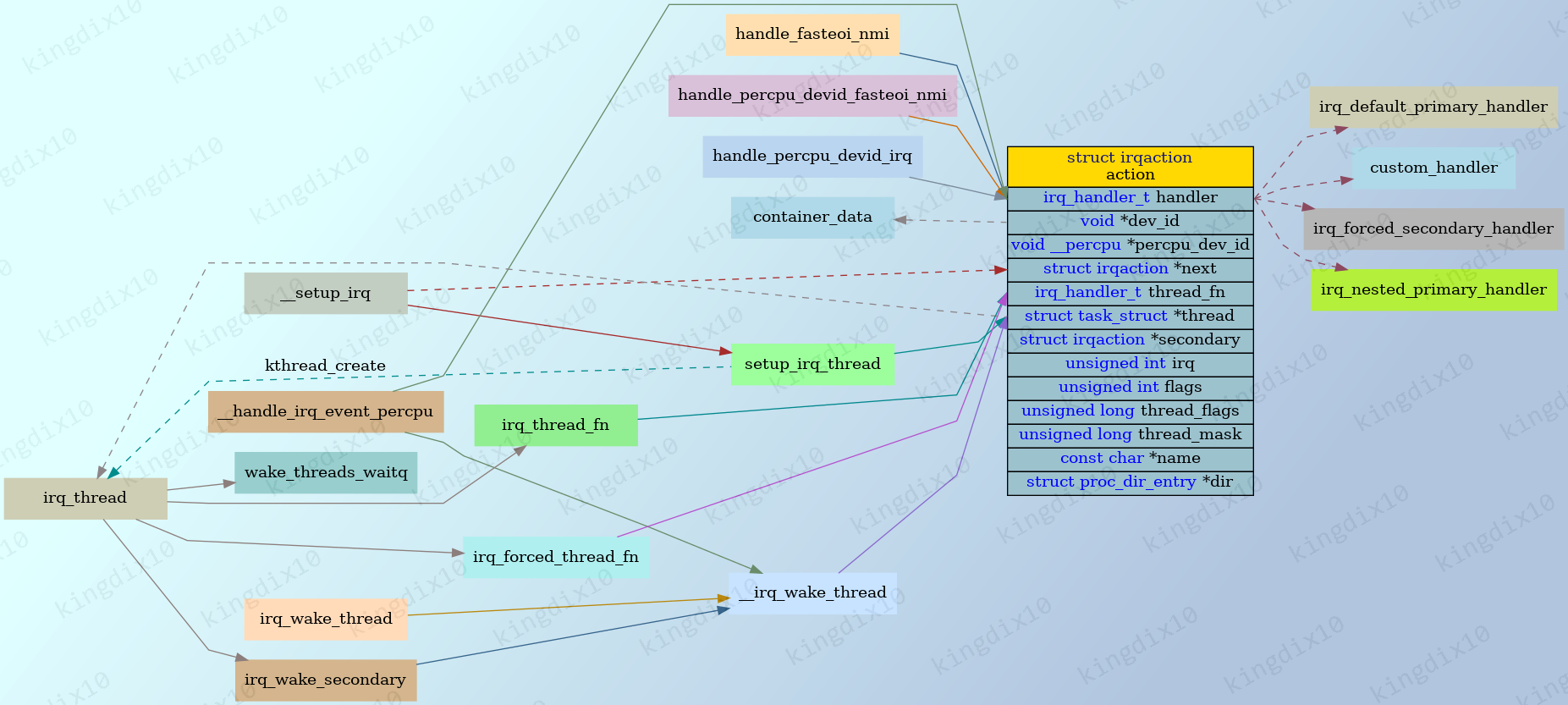
1/// include/linux/interrupt.h
2/**
3 * struct irqaction - per interrupt action descriptor
4 * @handler: interrupt handler function
5 * @name: name of the device
6 * @dev_id: cookie to identify the device
7 * @percpu_dev_id: cookie to identify the device
8 * @next: pointer to the next irqaction for shared interrupts
9 * @irq: interrupt number
10 * @flags: flags (see IRQF_* above)
11 * @thread_fn: interrupt handler function for threaded interrupts
12 * @thread: thread pointer for threaded interrupts
13 * @secondary: pointer to secondary irqaction (force threading)
14 * @thread_flags: flags related to @thread
15 * @thread_mask: bitmask for keeping track of @thread activity
16 * @dir: pointer to the proc/irq/NN/name entry
17 */
18struct irqaction {
19 irq_handler_t handler;
20 void *dev_id;
21 void __percpu *percpu_dev_id;
22 struct irqaction *next;
23 irq_handler_t thread_fn;
24 struct task_struct *thread;
25 struct irqaction *secondary;
26 unsigned int irq;
27 unsigned int flags;
28 unsigned long thread_flags;
29 unsigned long thread_mask;
30 const char *name;
31 struct proc_dir_entry *dir;
32} ____cacheline_internodealigned_in_smp;
2. __setup_irq
__setup_irq的代码量比较多,整理其主要流程如下:
- 如果支持使用中断线程化,使用
setup_irq_thread修改irqaction的handler。 - 如果直接已经为中断添加过irqaction,将新的irqaction挂到
struct irqaction单链表的最后。 - 如果是第一次申请中断,根据需要设置厨房类型、激活中断,并进行一下其他配置。
1/// kernel/irq/manage.c
2/*
3 * Internal function to register an irqaction - typically used to
4 * allocate special interrupts that are part of the architecture.
5 *
6 * Locking rules:
7 *
8 * desc->request_mutex Provides serialization against a concurrent free_irq()
9 * chip_bus_lock Provides serialization for slow bus operations
10 * desc->lock Provides serialization against hard interrupts
11 *
12 * chip_bus_lock and desc->lock are sufficient for all other management and
13 * interrupt related functions. desc->request_mutex solely serializes
14 * request/free_irq().
15 */
16static int
17__setup_irq(unsigned int irq, struct irq_desc *desc, struct irqaction *new)
18{
19 struct irqaction *old, **old_ptr;
20 unsigned long flags, thread_mask = 0;
21 int ret, nested, shared = 0;
22
23 /// ... ...
24
25 new->irq = irq;
26
27 /*
28 * If the trigger type is not specified by the caller,
29 * then use the default for this interrupt.
30 */
31 if (!(new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK))
32 new->flags |= irqd_get_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data);
33
34 /*
35 * Check whether the interrupt nests into another interrupt
36 * thread.
37 */
38 nested = irq_settings_is_nested_thread(desc);
39 if (nested) {
40 /// ... ...
41 } else {
42 if (irq_settings_can_thread(desc)) {
43 ret = irq_setup_forced_threading(new);
44 if (ret)
45 goto out_mput;
46 }
47 }
48
49 /*
50 * Create a handler thread when a thread function is supplied
51 * and the interrupt does not nest into another interrupt
52 * thread.
53 */
54 if (new->thread_fn && !nested) {
55 ret = setup_irq_thread(new, irq, false);
56 if (ret)
57 goto out_mput;
58 if (new->secondary) {
59 ret = setup_irq_thread(new->secondary, irq, true);
60 if (ret)
61 goto out_thread;
62 }
63 }
64
65 /*
66 * Drivers are often written to work w/o knowledge about the
67 * underlying irq chip implementation, so a request for a
68 * threaded irq without a primary hard irq context handler
69 * requires the ONESHOT flag to be set. Some irq chips like
70 * MSI based interrupts are per se one shot safe. Check the
71 * chip flags, so we can avoid the unmask dance at the end of
72 * the threaded handler for those.
73 */
74 if (desc->irq_data.chip->flags & IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE)
75 new->flags &= ~IRQF_ONESHOT;
76
77 /*
78 * Protects against a concurrent __free_irq() call which might wait
79 * for synchronize_hardirq() to complete without holding the optional
80 * chip bus lock and desc->lock. Also protects against handing out
81 * a recycled oneshot thread_mask bit while it's still in use by
82 * its previous owner.
83 */
84 mutex_lock(&desc->request_mutex);
85
86 /*
87 * Acquire bus lock as the irq_request_resources() callback below
88 * might rely on the serialization or the magic power management
89 * functions which are abusing the irq_bus_lock() callback,
90 */
91 chip_bus_lock(desc);
92
93 /* First installed action requests resources. */
94 if (!desc->action) {
95 ret = irq_request_resources(desc);
96 if (ret) {
97 pr_err("Failed to request resources for %s (irq %d) on irqchip %s\n",
98 new->name, irq, desc->irq_data.chip->name);
99 goto out_bus_unlock;
100 }
101 }
102
103 /*
104 * The following block of code has to be executed atomically
105 * protected against a concurrent interrupt and any of the other
106 * management calls which are not serialized via
107 * desc->request_mutex or the optional bus lock.
108 */
109 raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&desc->lock, flags);
110 old_ptr = &desc->action;
111 old = *old_ptr;
112 if (old) {
113 /// ... ...
114
115 /* add new interrupt at end of irq queue */
116 do {
117 /*
118 * Or all existing action->thread_mask bits,
119 * so we can find the next zero bit for this
120 * new action.
121 */
122 thread_mask |= old->thread_mask;
123 old_ptr = &old->next;
124 old = *old_ptr;
125 } while (old);
126 shared = 1;
127 }
128
129 /*
130 * Setup the thread mask for this irqaction for ONESHOT. For
131 * !ONESHOT irqs the thread mask is 0 so we can avoid a
132 * conditional in irq_wake_thread().
133 */
134 if (new->flags & IRQF_ONESHOT) {
135 /*
136 * Unlikely to have 32 resp 64 irqs sharing one line,
137 * but who knows.
138 */
139 if (thread_mask == ~0UL) {
140 ret = -EBUSY;
141 goto out_unlock;
142 }
143 /*
144 * The thread_mask for the action is or'ed to
145 * desc->thread_active to indicate that the
146 * IRQF_ONESHOT thread handler has been woken, but not
147 * yet finished. The bit is cleared when a thread
148 * completes. When all threads of a shared interrupt
149 * line have completed desc->threads_active becomes
150 * zero and the interrupt line is unmasked. See
151 * handle.c:irq_wake_thread() for further information.
152 *
153 * If no thread is woken by primary (hard irq context)
154 * interrupt handlers, then desc->threads_active is
155 * also checked for zero to unmask the irq line in the
156 * affected hard irq flow handlers
157 * (handle_[fasteoi|level]_irq).
158 *
159 * The new action gets the first zero bit of
160 * thread_mask assigned. See the loop above which or's
161 * all existing action->thread_mask bits.
162 */
163 new->thread_mask = 1UL << ffz(thread_mask);
164
165 } else if (new->handler == irq_default_primary_handler &&
166 !(desc->irq_data.chip->flags & IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE)) {
167 /*
168 * The interrupt was requested with handler = NULL, so
169 * we use the default primary handler for it. But it
170 * does not have the oneshot flag set. In combination
171 * with level interrupts this is deadly, because the
172 * default primary handler just wakes the thread, then
173 * the irq lines is reenabled, but the device still
174 * has the level irq asserted. Rinse and repeat....
175 *
176 * While this works for edge type interrupts, we play
177 * it safe and reject unconditionally because we can't
178 * say for sure which type this interrupt really
179 * has. The type flags are unreliable as the
180 * underlying chip implementation can override them.
181 */
182 pr_err("Threaded irq requested with handler=NULL and !ONESHOT for %s (irq %d)\n",
183 new->name, irq);
184 ret = -EINVAL;
185 goto out_unlock;
186 }
187
188 if (!shared) {
189 /* Setup the type (level, edge polarity) if configured: */
190 if (new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK) {
191 ret = __irq_set_trigger(desc,
192 new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK);
193
194 if (ret)
195 goto out_unlock;
196 }
197
198 /*
199 * Activate the interrupt. That activation must happen
200 * independently of IRQ_NOAUTOEN. request_irq() can fail
201 * and the callers are supposed to handle
202 * that. enable_irq() of an interrupt requested with
203 * IRQ_NOAUTOEN is not supposed to fail. The activation
204 * keeps it in shutdown mode, it merily associates
205 * resources if necessary and if that's not possible it
206 * fails. Interrupts which are in managed shutdown mode
207 * will simply ignore that activation request.
208 */
209 ret = irq_activate(desc);
210 if (ret)
211 goto out_unlock;
212
213 desc->istate &= ~(IRQS_AUTODETECT | IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED | \
214 IRQS_ONESHOT | IRQS_WAITING);
215 irqd_clear(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS);
216
217 if (new->flags & IRQF_PERCPU) {
218 irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_PER_CPU);
219 irq_settings_set_per_cpu(desc);
220 if (new->flags & IRQF_NO_DEBUG)
221 irq_settings_set_no_debug(desc);
222 }
223
224 if (noirqdebug)
225 irq_settings_set_no_debug(desc);
226
227 if (new->flags & IRQF_ONESHOT)
228 desc->istate |= IRQS_ONESHOT;
229
230 /* Exclude IRQ from balancing if requested */
231 if (new->flags & IRQF_NOBALANCING) {
232 irq_settings_set_no_balancing(desc);
233 irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_NO_BALANCING);
234 }
235
236 if (!(new->flags & IRQF_NO_AUTOEN) &&
237 irq_settings_can_autoenable(desc)) {
238 irq_startup(desc, IRQ_RESEND, IRQ_START_COND);
239 } else {
240 /*
241 * Shared interrupts do not go well with disabling
242 * auto enable. The sharing interrupt might request
243 * it while it's still disabled and then wait for
244 * interrupts forever.
245 */
246 WARN_ON_ONCE(new->flags & IRQF_SHARED);
247 /* Undo nested disables: */
248 desc->depth = 1;
249 }
250
251 } else if (new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK) {
252 unsigned int nmsk = new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK;
253 unsigned int omsk = irqd_get_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data);
254
255 if (nmsk != omsk)
256 /* hope the handler works with current trigger mode */
257 pr_warn("irq %d uses trigger mode %u; requested %u\n",
258 irq, omsk, nmsk);
259 }
260
261 *old_ptr = new;
262
263 irq_pm_install_action(desc, new);
264
265 /* Reset broken irq detection when installing new handler */
266 desc->irq_count = 0;
267 desc->irqs_unhandled = 0;
268
269 /*
270 * Check whether we disabled the irq via the spurious handler
271 * before. Reenable it and give it another chance.
272 */
273 if (shared && (desc->istate & IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED)) {
274 desc->istate &= ~IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED;
275 __enable_irq(desc);
276 }
277
278 raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&desc->lock, flags);
279 chip_bus_sync_unlock(desc);
280 mutex_unlock(&desc->request_mutex);
281
282 irq_setup_timings(desc, new);
283
284 wake_up_and_wait_for_irq_thread_ready(desc, new);
285 wake_up_and_wait_for_irq_thread_ready(desc, new->secondary);
286
287 register_irq_proc(irq, desc);
288 new->dir = NULL;
289 register_handler_proc(irq, new);
290 return 0;
291
292///... ...
293}
2.1. 默认handler
1/// kernel/irq/manage.c
2/*
3 * Default primary interrupt handler for threaded interrupts. Is
4 * assigned as primary handler when request_threaded_irq is called
5 * with handler == NULL. Useful for oneshot interrupts.
6 */
7/// 用于唤醒默认的中断处理线程
8static irqreturn_t irq_default_primary_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
9{
10 return IRQ_WAKE_THREAD;
11}
12
13/*
14 * Primary handler for nested threaded interrupts. Should never be
15 * called.
16 */
17static irqreturn_t irq_nested_primary_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
18{
19 WARN(1, "Primary handler called for nested irq %d\n", irq);
20 return IRQ_NONE;
21}
22
23static irqreturn_t irq_forced_secondary_handler(int irq, void *dev_id)
24{
25 WARN(1, "Secondary action handler called for irq %d\n", irq);
26 return IRQ_NONE;
27}
3. 中断线程
在不是中断嵌套的清闲,如果同时指定了handler和thread_fn,或者使能了强制中断线程化,__setup_irq会通过setup_irq_thread来设置中断线程,其代码如下
1/// kernel/irq/manage.c
2static int
3setup_irq_thread(struct irqaction *new, unsigned int irq, bool secondary)
4{
5 struct task_struct *t;
6
7 if (!secondary) {
8 t = kthread_create(irq_thread, new, "irq/%d-%s", irq,
9 new->name);
10 } else {
11 t = kthread_create(irq_thread, new, "irq/%d-s-%s", irq,
12 new->name);
13 }
14
15 if (IS_ERR(t))
16 return PTR_ERR(t);
17
18 /*
19 * We keep the reference to the task struct even if
20 * the thread dies to avoid that the interrupt code
21 * references an already freed task_struct.
22 */
23 new->thread = get_task_struct(t);
24 /*
25 * Tell the thread to set its affinity. This is
26 * important for shared interrupt handlers as we do
27 * not invoke setup_affinity() for the secondary
28 * handlers as everything is already set up. Even for
29 * interrupts marked with IRQF_NO_BALANCE this is
30 * correct as we want the thread to move to the cpu(s)
31 * on which the requesting code placed the interrupt.
32 */
33 set_bit(IRQTF_AFFINITY, &new->thread_flags);
34 return 0;
35}
3.1. 强制中断线程化
如果是强制中断线程化,会将irqaction的handler设为irq_default_primary_handler,而将原来的handler赋给thread_fn。
如果原来的handler和thread_fn均被设置,则会申请新的irqaction作为new->secondary。将thread_fn赋值给new->secondary->thread_fn,new->secondary->handler设为irq_forced_secondary_handler。
1/// kernel/irq/manage.c
2static int irq_setup_forced_threading(struct irqaction *new)
3{
4 if (!force_irqthreads())
5 return 0;
6 if (new->flags & (IRQF_NO_THREAD | IRQF_PERCPU | IRQF_ONESHOT))
7 return 0;
8
9 /*
10 * No further action required for interrupts which are requested as
11 * threaded interrupts already
12 */
13 if (new->handler == irq_default_primary_handler)
14 return 0;
15
16 new->flags |= IRQF_ONESHOT;
17
18 /*
19 * Handle the case where we have a real primary handler and a
20 * thread handler. We force thread them as well by creating a
21 * secondary action.
22 */
23 if (new->handler && new->thread_fn) {
24 /* Allocate the secondary action */
25 new->secondary = kzalloc(sizeof(struct irqaction), GFP_KERNEL);
26 if (!new->secondary)
27 return -ENOMEM;
28 new->secondary->handler = irq_forced_secondary_handler;
29 new->secondary->thread_fn = new->thread_fn;
30 new->secondary->dev_id = new->dev_id;
31 new->secondary->irq = new->irq;
32 new->secondary->name = new->name;
33 }
34 /* Deal with the primary handler */
35 set_bit(IRQTF_FORCED_THREAD, &new->thread_flags);
36 new->thread_fn = new->handler;
37 new->handler = irq_default_primary_handler;
38 return 0;
39}
强制中断线程化配置
irq_setup_forced_threading会调用force_irqthreads判断系统是否开启强制中断线程化。
1#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_FORCED_THREADING
2# ifdef CONFIG_PREEMPT_RT
3# define force_irqthreads() (true)
4# else
5/// static_key支持动态开关,原理见jump label分析
6DECLARE_STATIC_KEY_FALSE(force_irqthreads_key);
7# define force_irqthreads() (static_branch_unlikely(&force_irqthreads_key))
8# endif
9#else
10#define force_irqthreads() (false)
11#endif




