1. timekeeping
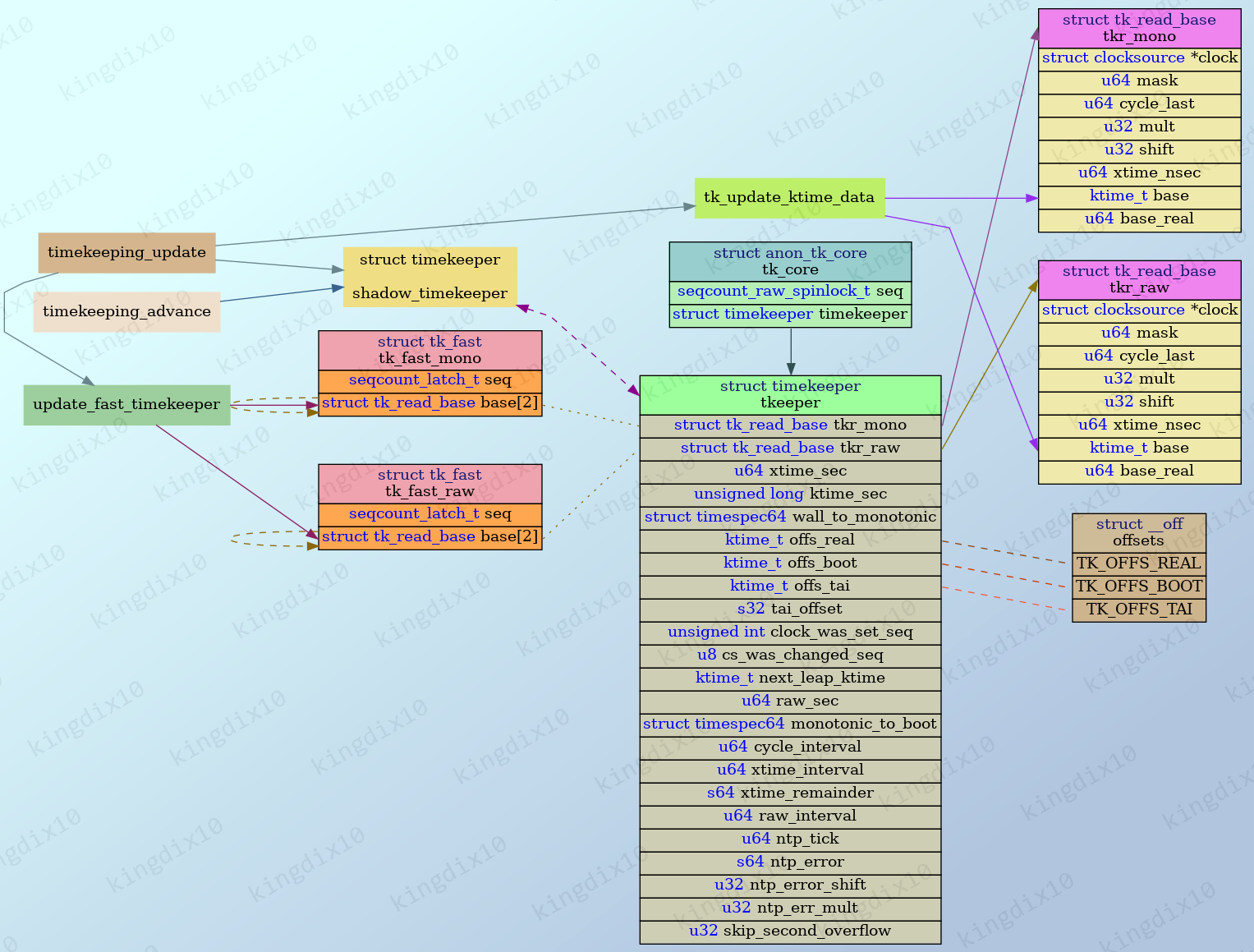
timekeeping是时间子系统用于从clocksource获取时间,维护墙上时间、单调递增时间、启动时间的模块,timekeeping提供了各种时间的获取接口。其核心数据为tk_core,实现了对timekeeper的加锁访问。
1/*
2 * The most important data for readout fits into a single 64 byte
3 * cache line.
4 */
5static struct {
6 seqcount_raw_spinlock_t seq;
7 struct timekeeper timekeeper;
8} tk_core ____cacheline_aligned = {
9 .seq = SEQCNT_RAW_SPINLOCK_ZERO(tk_core.seq, &timekeeper_lock),
10};
11
12static struct timekeeper shadow_timekeeper;
timekeeping_init主要就是在对tk_core.timekeeper进行初始化。下面是timekeeping_init函数总体流程
- read_persistent_wall_and_boot_offset读取wall_time和boot_offest。默认为0。1
- 验证wall_time和boot_offset是否正确,不正确则设置为0
- 计算wall_to_mono
- 获取锁,开始修改tk
- ntp_init(Network Time Protocol)
- clocksource_default_clock获取默认clock并enable,clocksource默认为clocksource_jiffies,在probe timer后会切换clocksource
- tk_setup_internals、tk_set_xtime、tk_set_wall_to_mono和timekeeping_update设置tk
- 释放锁
2. 计算墙上时间、启动时间差值
wall_time墙上时间:自然时间,也就是真实世界的时间。timekeeper里用xtime表示。
boot_time:系统启动的时间
1boot_offset = wall_time - boot_time
2wall_time + wall_to_mono = boot_time
read_persistent_wall_and_boot_offset读取时钟,这个函数是一个 __weak的函数,默认设置wall_time和boot_offset为0,如果支持rtc时钟,可以读取rtc时钟里的值。
校验wall_time的正确性,如果时间格式正确,而且不为0,则表示有断电不失效的时钟,则设置persistent_clock_exists为true,否则,wall_time必须为0。
校验完wall_time后,再检查boot_offset是否正确,boot_offset不能比wall_time还要晚。
wall_to_mono,将墙上时间转为单调递增时间。单调递增时间是即从某个时间点开始到现在过去的时间。用户不能修改这个时间,但是当系统进入休眠(suspend)时,时间也不会增加的。更改系统时间也不会对mono时间产生影响。
接下来就是比较重要的初始化timekeeper的部分了。
3. timekeeper初始化
tk_core.timekeeper受自旋锁timekeeper_lock和读写顺序锁tk_core.seq保护。
首先需要获取锁。
ntp_init,ntp(Network Time Protocol,网络时间协议)相关初始化,暂不分析。
3.1. 默认时钟源
clocksource_default_clock用于获取默认时钟源,这是一个 __weak函数,默认使用clocksource_jiffies作为时钟源,精度很低,如果有更精确的时钟源,可以重新实现此函数。这里设置一个时钟源,是为了防止调用获取时间的接口时出现问题。后续有新的时钟源注册时,会替换掉低精度的时钟源。
1/*
2 * The Jiffies based clocksource is the lowest common
3 * denominator clock source which should function on
4 * all systems. It has the same coarse resolution as
5 * the timer interrupt frequency HZ and it suffers
6 * inaccuracies caused by missed or lost timer
7 * interrupts and the inability for the timer
8 * interrupt hardware to accurately tick at the
9 * requested HZ value. It is also not recommended
10 * for "tick-less" systems.
11 */
12static struct clocksource clocksource_jiffies = {
13 .name = "jiffies",
14 .rating = 1, /* lowest valid rating*/
15 .uncertainty_margin = 32 * NSEC_PER_MSEC,
16 .read = jiffies_read,
17 .mask = CLOCKSOURCE_MASK(32),
18 .mult = TICK_NSEC << JIFFIES_SHIFT, /* details above */
19 .shift = JIFFIES_SHIFT,
20 .max_cycles = 10,
21};
获取时钟源后,如果该时钟源有enable回调,则需要调用该函数来使能。
3.2. tk_setup_internals
tk_setup_internals来初始化tk_core.timekeeper的一些内部成员。
其中比较中要的是tkr_mono和tkr_raw,使用默认时钟对这两个成员初始化,用于给获取时间的接口提供时钟源,比如ktime_get接口。在后续有更高精度的时钟之后,会进行更新。
3.3. 设置时间
tk_set_xtime墙上时间
根据之前计算出的wall_time设置tk_core.timekeeper的xtime_sec和tkr_mono.xtime_nsec。
tk->raw_sec = 0,这是CLOCK_MONOTONIC_RAW
根据之前计算出的wall_to_mono,调用tk_set_wall_to_mono设置一些offs_real和offs_tai,这些offset在调用时间获取接口时会用到。
1static void tk_set_wall_to_mono(struct timekeeper *tk, struct timespec64 wtm)
2{
3 struct timespec64 tmp;
4
5 /*
6 * Verify consistency of: offset_real = -wall_to_monotonic
7 * before modifying anything
8 */
9 set_normalized_timespec64(&tmp, -tk->wall_to_monotonic.tv_sec,
10 -tk->wall_to_monotonic.tv_nsec);
11 WARN_ON_ONCE(tk->offs_real != timespec64_to_ktime(tmp));
12 tk->wall_to_monotonic = wtm;
13 set_normalized_timespec64(&tmp, -wtm.tv_sec, -wtm.tv_nsec);
14 tk->offs_real = timespec64_to_ktime(tmp);
15 tk->offs_tai = ktime_add(tk->offs_real, ktime_set(tk->tai_offset, 0));
16}
4. timekeeping_update
timekeeping_update是最终完成各种时间基准初始化的函数。
1/* must hold timekeeper_lock */
2static void timekeeping_update(struct timekeeper *tk, unsigned int action)
3{
4 if (action & TK_CLEAR_NTP) {
5 tk->ntp_error = 0;
6 ntp_clear();
7 }
8
9 tk_update_leap_state(tk);
10 tk_update_ktime_data(tk);
11
12 update_vsyscall(tk);
13 update_pvclock_gtod(tk, action & TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET);
14
15 tk->tkr_mono.base_real = tk->tkr_mono.base + tk->offs_real;
16 update_fast_timekeeper(&tk->tkr_mono, &tk_fast_mono);
17 update_fast_timekeeper(&tk->tkr_raw, &tk_fast_raw);
18
19 if (action & TK_CLOCK_WAS_SET)
20 tk->clock_was_set_seq++;
21 /*
22 * The mirroring of the data to the shadow-timekeeper needs
23 * to happen last here to ensure we don't over-write the
24 * timekeeper structure on the next update with stale data
25 */
26 if (action & TK_MIRROR)
27 memcpy(&shadow_timekeeper, &tk_core.timekeeper,
28 sizeof(tk_core.timekeeper));
29}
tk_update_leap_state闰秒调整
4.1. tk_update_ktime_data:tkr_mono和tkr_raw设置
tk->tkr_mono.base
tk->tkr_raw.base
tk->ktime_sec
tk->tkr_mono.base_real = tk->tkr_mono.base + tk->offs_real
4.2. update_fast_timekeeper
除了tkr_mono和tkr_raw两个struct tk_read_base,linux内核还定义了两个struct tk_fast,tk_fast_mono和tk_fast_raw。这两个是用来实现NMI safe的。
1/**
2 * struct tk_fast - NMI safe timekeeper
3 * @seq: Sequence counter for protecting updates. The lowest bit
4 * is the index for the tk_read_base array
5 * @base: tk_read_base array. Access is indexed by the lowest bit of
6 * @seq.
7 *
8 * See @update_fast_timekeeper() below.
9 */
10struct tk_fast {
11 seqcount_latch_t seq;
12 struct tk_read_base base[2];
13};
1/*
2 * Boot time initialization which allows local_clock() to be utilized
3 * during early boot when clocksources are not available. local_clock()
4 * returns nanoseconds already so no conversion is required, hence mult=1
5 * and shift=0. When the first proper clocksource is installed then
6 * the fast time keepers are updated with the correct values.
7 */
8define FAST_TK_INIT \
9 { \
10 .clock = &dummy_clock, \
11 .mask = CLOCKSOURCE_MASK(64), \
12 .mult = 1, \
13 .shift = 0, \
14 }
15
16static struct tk_fast tk_fast_mono ____cacheline_aligned = {
17 .seq = SEQCNT_LATCH_ZERO(tk_fast_mono.seq),
18 .base[0] = FAST_TK_INIT,
19 .base[1] = FAST_TK_INIT,
20};
21
22static struct tk_fast tk_fast_raw ____cacheline_aligned = {
23 .seq = SEQCNT_LATCH_ZERO(tk_fast_raw.seq),
24 .base[0] = FAST_TK_INIT,
25 .base[1] = FAST_TK_INIT,
26};
可以对比一下,访问tkr_mono和tkr_raw时,用的是read_seqcount_begin和read_seqcount_retry,而访问tk_fast_mono和tk_fast_raw用的是raw_read_seqcount_latch和read_seqcount_latch_retry。
具体可以看内核ktime_get_mono_fast_ns和ktime_get_raw_fast_ns等函数的解释。
1 update_fast_timekeeper(&tk->tkr_mono, &tk_fast_mono);
2 update_fast_timekeeper(&tk->tkr_raw, &tk_fast_raw);
以tk_fast_mono为例,update_fast_timekeeper是把timekeeper的tkr_mono复制到
tk_fast_mono的base数组,保存两份是为了保证在修改一个时,可以用另一个来获取正确的数值。
4.3. shadow_timekeeper
如果action指定了TK_MIRROR,则将tk_core.timekeeper备份到shadow_timekeeper,shadow_timekeeper可以用于在resume后恢复timekeeper。这个动作需要在最后进行,以确保在下一次更新时不会用过时的数据重写timekeeper。
最后再释放一下锁,这样timekeeping就初始化好了。
在timer_probe时,会注册精度更高的clocksource,这样就可以获取各种时间。